RICE DISEASES AND MANAGEMENTS
AN INTRODUCTION TO RICE DISEASES
Paddy diseases and their management are critical for ensuring healthy crop yields. Among the notable diseases affecting paddy are brown leaf spots, bacterial leaf blight, sheath blight, paddy blast, paddy blight, and stem rot. Each of these diseases presents unique symptoms and requires specific prevention strategies to mitigate their impact on crop health.
فصل کی صحت مند پیداوار کو یقینی بنانے کے لیے دھان کی بیماریاں اور ان کا انتظام بہت ضروری ہے۔ دھان کو متاثر کرنے والی قابل ذکر بیماریوں میں پتوں کے بھورے دھبے، بیکٹیریل لیف بلائیٹ، شیتھ بلائیٹ، پیڈی بلاسٹ، دھان کی خرابی اور تنے کا سڑنا شامل ہیں۔ ان بیماریوں میں سے ہر ایک منفرد علامات پیش کرتا ہے اور فصل کی صحت پر ان کے اثرات کو کم کرنے کے لیے مخصوص روک تھام کی حکمت عملیوں کی ضرورت ہوتی ہے۔
1-Brown Leaf Spot of Rice
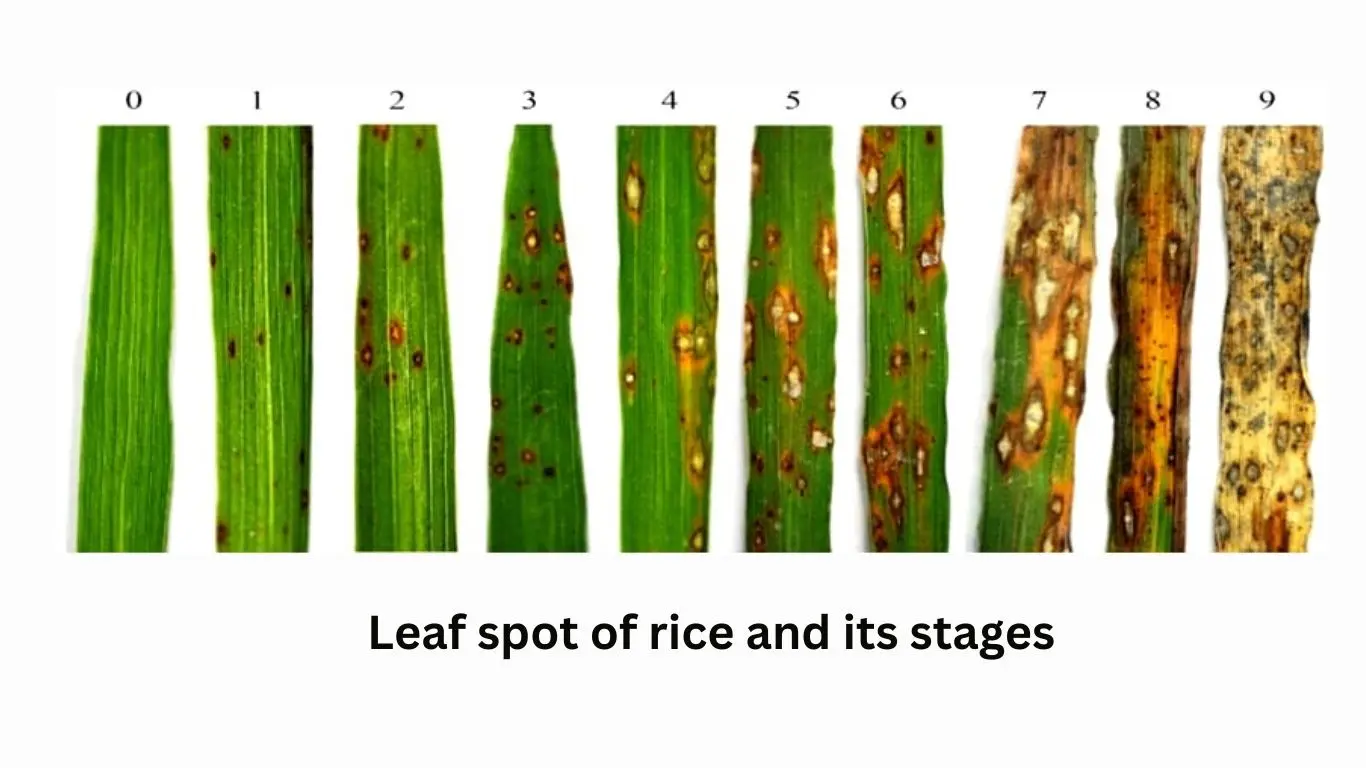
Brown leaf spots, primarily caused by the fungus Bipolaris oryzae, affect both basmati and non-basmati rice varieties, particularly in fields lacking sufficient potash. The disease manifests as small, round, or oval lesions on the leaves, characterized by brown edges and gray centers. In severe cases, the lesions proliferate extensively, and when grains are affected, they develop dark brown, slightly rounded or oblong spots. The appearance of these spots can create a clustered look on the panicles when viewed from a distance.
بھورے پتوں کے دھبے، بنیادی طور پر فنگس Bipolaris oryzae کی وجہ سے، باسمتی اور غیر باسمتی چاول کی دونوں اقسام کو متاثر کرتے ہیں، خاص طور پر ان کھیتوں میں جہاں کافی پوٹاش کی کمی ہوتی ہے۔ یہ بیماری پتوں پر چھوٹے، گول یا بیضوی گھاووں کے طور پر ظاہر ہوتی ہے، جس کی خصوصیات بھورے کناروں اور سرمئی مراکز سے ہوتی ہے۔ شدید حالتوں میں، گھاو بڑے پیمانے پر پھیلتے ہیں، اور جب دانے متاثر ہوتے ہیں، تو ان پر گہرے بھورے، ہلکے گول یا لمبے دھبے بن جاتے ہیں۔ دور سے دیکھنے پر ان دھبوں کی ظاہری شکل پینکلز پر ایک جھرمٹ کی شکل پیدا کر سکتی ہے۔
Management of Brown Leaf Spots:
To combat brown leaf spots, it is essential to utilize disease-free seeds and follow the guidance of local agricultural extension services regarding fungicide application. Adequate fertilization with nitrogen, phosphorus, and potash is also crucial. Upon observing symptoms, it is recommended to apply a mixture of Trifloxystrobin +tebuconazole at a rate of 65 grams, or alternatively, Difenaconazole at 125 ml along with sulfur at 800 grams per acre to effectively manage the disease.
بھورے پتوں کے دھبوں کا مقابلہ کرنے کے لیے، بیماری سے پاک بیجوں کا استعمال کرنا اور فنگسائڈ کے استعمال کے حوالے سے مقامی زرعی توسیعی خدمات کی رہنمائی پر عمل کرنا ضروری ہے۔ نائٹروجن، فاسفورس اور پوٹاش کے ساتھ مناسب کھاد بھی بہت ضروری ہے۔ علامات کا مشاہدہ کرنے پر، یہ تجویز کیا جاتا ہے کہ بیماری پر مؤثر طریقے سے قابو پانے کے لیے Trifloxystrobin+tebuconazoleکا مرکب کے ساتھ 65 گرام، یا متبادل طور پر، Difenaconazole 125 ملی لیٹر اور سلفر 800 گرام فی ایکڑ کے حساب سے استعمال کریں۔
Sr.no | Name of Agricultural Pesticide | Disease | Amount per acre | ETL Level | Group |
1 | Difenoconazole 250 EC | Rice Blight (Bhabka) | 125 ml | 14 | 3 |
2 | Azoxystrobin 25% | Rice Blight (Bhabka) | 180 ml | 28 | 11 |
3 | Difenoconazole +Azoxystrobin 30% EC | Rice blight , Brown Spots and Leaf Spots | 200 ml | 14-7 | 24 |
4 | Hexaconazole 51 EC | leaf spots | 400ml | 21 | 3 |
5 | bacterial blight, blight, leaf spots | 300 gm | 3-7 | 24 | |
6 | azoxystrobin +difenoconazole 32.5 5 SC | 200ML | 200ml | 7-14 | 3+11 |
7 | trifloxystrobin +tebuconazole 75wp | blight, brown spots | 65gm | 35 | 3+11 |
8 | azoxystrobin +propeconazole 32%sc | leaf spots | 200gram | 35 | 3+11 |
9 | azoxystrobin + tebuconazole 50% sc | leaf spots | 250 gm | 28 | 3+11 |
10 | validamicie + difenoconazole 12 wp | blight | 200gm | 14-35 | 3+18 |
11 | copper hydroxide 77%wp | bacterial blight | 200gm | 14 | M01 |
12 | copper oxychloride 50%wg | bacterial blight | 250gm | 14 | M01 |
13 | bacterial blight,blight,brown leaf spots | 800 gm | 5-7 | M02 | |
14 | Validamacine 10% SL | Leaf Spot | 400Ml | 14-35 | U18 |
2-Bacterial Leaf Blight of Rice
Bacterial leaf blight is a disease caused by the bacterium Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, which manifests during the budding stage of the crop. The initial symptoms are observed at the tips and edges of the leaves, where the disease begins to spread both in length and width, ultimately affecting the healthier portions of the plant. The affected leaves exhibit white, moist streaks, which subsequently dry out, turning white and curling upwards. Initially, the disease presents itself in patches, but under favorable environmental conditions, it can proliferate and encompass the entire crop, giving it a scorched appearance from a distance. This affliction leads to a significant reduction in grain production and overall yield.
بیکٹیریل لیف بلائٹ ایک بیماری ہے جو بیکٹیریم Xanthomonas oryzae pv کی وجہ سے ہوتی ہے۔ oryzae، جو فصل کے ابھرنے کے مرحلے کے دوران ظاہر ہوتا ہے۔ ابتدائی علامات کا مشاہدہ پتوں کے سروں اور کناروں پر ہوتا ہے، جہاں بیماری لمبائی اور چوڑائی دونوں میں پھیلنا شروع کر دیتی ہے، جو بالآخر پودے کے صحت مند حصوں کو متاثر کرتی ہے۔ متاثرہ پتے سفید، نم لکیریں دکھاتے ہیں، جو بعد میں سوکھ جاتے ہیں، سفید ہو جاتے ہیں اور اوپر کی طرف جھک جاتے ہیں۔ ابتدائی طور پر، بیماری اپنے آپ کو پیچ کی شکل میں ظاہر کرتی ہے، لیکن سازگار ماحولیاتی حالات میں، یہ پھیل سکتی ہے اور پوری فصل کو گھیر سکتی ہے، جس سے اسے دور سے جھلسا ہوا نظر آتا ہے۔ یہ مصیبت اناج کی پیداوار اور مجموعی پیداوار میں نمایاں کمی کا باعث بنتی ہے۔
Managements of Bacterial Leaf Blight of Rice:
To manage bacterial leaf blight effectively, it is crucial to avoid the cultivation of unapproved or prohibited plant varieties. Timely transplantation of seedlings is essential, with a recommendation to use seedlings that are 25 to 35 days old. Care should be taken to prevent injury to the seedlings during this process, and it is advisable to irrigate the field a day prior to uprooting to minimize root damage. Additionally, it is important to prevent water from infected fields from flowing into healthy ones to avoid the spread of the disease. Maintaining a water level of 1 to 3 inches in paddy fields and timely control of weeds can disrupt the life cycle of the pathogen and mitigate its spread.Furthermore, effective pest management, particularly targeting leaf hoppers, is vital for controlling the disease. Early identification of the disease allows for the removal of infected plants, along with a few adjacent healthy ones, to limit further infection. Enhancing plant immunity through the application of potash and the strategic use of nitrogenous fertilizers in three equal doses—at 25 days, 50 days after land preparation, and at transplanting—is recommended. In cases of severe infection, the application of peroxychloride or perhydroxide, along with kasugamycin, can be employed as a treatment to protect the crop.
بیکٹیریل پتوں کے جھلسنے کے مؤثر طریقے سے انتظام کرنے کے لیے، غیر منظور شدہ یا ممنوعہ پودوں کی اقسام کی کاشت سے بچنا بہت ضروری ہے۔ پودوں کی بروقت پیوند کاری ضروری ہے، اس کے ساتھ 25 سے 35 دن پرانے پودوں کے استعمال کی سفارش کی جاتی ہے۔ اس عمل کے دوران بیجوں کو چوٹ سے بچنے کے لیے احتیاط کی جانی چاہیے، اور جڑ کے نقصان کو کم سے کم کرنے کے لیے اکھاڑ پھینکنے سے ایک دن پہلے کھیت کو سیراب کرنے کا مشورہ دیا جاتا ہے۔ مزید برآں، بیماری کے پھیلاؤ سے بچنے کے لیے متاثرہ کھیتوں کے پانی کو صحت مند کھیتوں میں جانے سے روکنا ضروری ہے۔ دھان کے کھیتوں میں پانی کی سطح کو 1 سے 3 انچ تک برقرار رکھنا اور جڑی بوٹیوں کا بروقت کنٹرول پیتھوجین کی زندگی کے چکر میں خلل ڈال سکتا ہے اور اس کے پھیلاؤ کو کم کر سکتا ہے۔ مزید برآں، کیڑوں کا موثر انتظام، خاص طور پر پتوں کے جھاڑیوں کو نشانہ بنانا، بیماری پر قابو پانے کے لیے بہت ضروری ہے۔ بیماری کی ابتدائی شناخت مزید انفیکشن کو محدود کرنے کے لیے، چند ملحقہ صحت مند پودوں کے ساتھ، متاثرہ پودوں کو ہٹانے کی اجازت دیتی ہے۔ پوٹاش کے استعمال کے ذریعے پودوں کی قوت مدافعت کو بڑھانے اور نائٹروجن والی کھادوں کے تین مساوی خوراکوں میں - 25 دن، زمین کی تیاری کے 50 دن بعد، اور پیوند کاری کے وقت - کی سفارش کی جاتی ہے۔ شدید انفیکشن کی صورت میں، کاسوگامائسن کے ساتھ پیروکسی کلورائیڈ یا پرہائیڈروکسائیڈ کا استعمال فصل کی حفاظت کے لیے بطور علاج استعمال کیا جا سکتا ہے۔
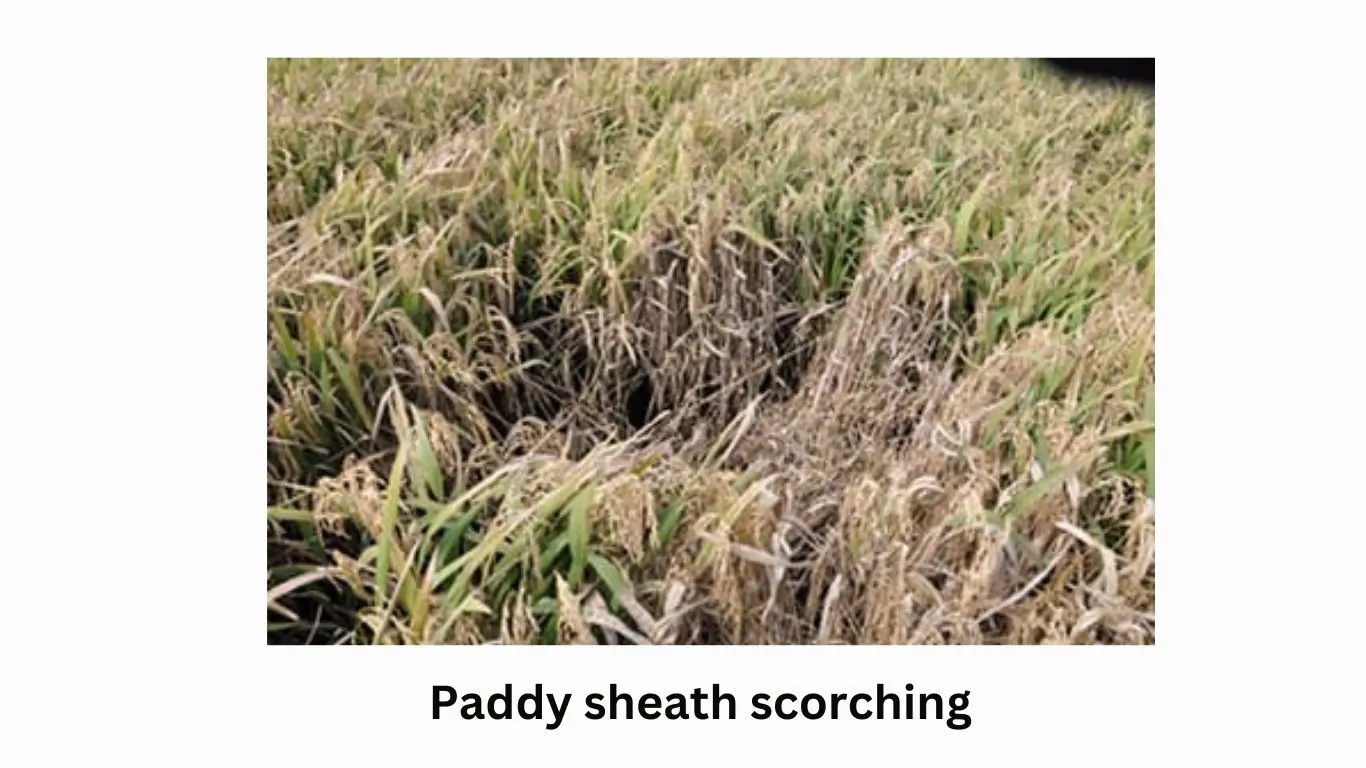
3-Paddy sheath scorching
This disease is caused by a fungus. At the beginning of the attack, 1 to 3 cm long and oval greenish-gray mottled spots appear on the surface of the leaf along the surface of the water, which later become irregularly whitish on the inside and slightly darker purple or purple on the edges. Reddish brown in color. In case of attack in the early stage of the crop, the ability of plants to form branches is reduced. In case of severe attack the leaves fall off. Due to the disease, the delivery of food to the grain is not done in the right amount, which affects the yield and quality. For remediation use a balanced application of fertilizers and spray recommended poisons.
یہ بیماری فنگس کی وجہ سے ہوتی ہے۔ حملے کے آغاز میں، پانی کی سطح کے ساتھ ساتھ پتے کی سطح پر 1 سے 3 سینٹی میٹر لمبے اور بیضوی سبز مائل بھوری رنگ کے دھبے نظر آتے ہیں، جو بعد میں اندر سے بے قاعدہ طور پر سفید اور کناروں پر قدرے گہرے جامنی یا جامنی رنگ کے ہو جاتے ہیں۔ . سرخی مائل بھورا رنگ۔ فصل کے ابتدائی مرحلے میں حملہ کی صورت میں پودوں کی شاخیں بنانے کی صلاحیت کم ہو جاتی ہے۔ شدید حملے کی صورت میں پتے جھڑ جاتے ہیں۔ بیماری کی وجہ سے اناج تک خوراک کی ترسیل صحیح مقدار میں نہیں ہوتی جس سے پیداوار اور معیار متاثر ہوتا ہے۔ تدارک کے لیے کھادوں کا متوازن استعمال کریں اور تجویز کردہ زہروں کا سپرے کریں۔
4-Rice Blast
This disease is caused by a fungus (Pyricularia oryzae). Its attack is more on Basmati varieties.It attacks the leaves, buds, neck and stem of the pod. The attack is severe in mirazmin fields which do not have the capacity to hold water. Eye-shaped marks are formed on the mole which are pointed on both sides. Its edges are dark brown and their middle part is clay colored. Under favorable conditions, these marks become large and coalesce and dry up large parts of the leaf, reducing the plant's ability to make food. In case of attack on the thorns, black marks are formed around them which surround it completely. The affected lump and the area above it dry up. In the case of an attack on the neck of the monger or on the mongers, the inky marks around it form a halo through which the food cannot reach the grains and the grains cannot be filled. Rash in case of severe attack.
یہ بیماری فنگس (Pyricularia oryzae) کی وجہ سے ہوتی ہے۔ اس کا حملہ باسمتی کی اقسام پر زیادہ ہوتا ہے۔ یہ پھلی کے پتوں، کلیوں، گردن اور تنے پر حملہ کرتا ہے۔ میرازمین کے کھیتوں میں حملہ شدید ہوتا ہے جن میں پانی رکھنے کی گنجائش نہیں ہوتی۔ آنکھ کی شکل کے نشان تل پر بنتے ہیں جو دونوں طرف نوکیلے ہوتے ہیں۔ اس کے کنارے گہرے بھورے اور درمیانی حصہ مٹی کا رنگ کا ہوتا ہے۔ سازگار حالات میں، یہ نشانات بڑے ہو جاتے ہیں اور اکٹھے ہو جاتے ہیں اور پتے کے بڑے حصوں کو خشک کر دیتے ہیں، جس سے پودے کی خوراک بنانے کی صلاحیت کم ہو جاتی ہے۔ کانٹوں پر حملہ ہونے کی صورت میں ان کے گرد سیاہ نشان بن جاتے ہیں جو اسے پوری طرح گھیر لیتے ہیں۔ متاثرہ گانٹھ اور اس کے اوپر والا حصہ سوکھ جاتا ہے۔ مونگر کی گردن پر یا منگر پر حملہ ہونے کی صورت میں اس کے گرد سیاہی کے نشان ایک ہالہ بن جاتے ہیں جس کے ذریعے کھانا اناج تک نہیں پہنچ سکتا اور اناج بھر نہیں سکتا۔ شدید حملے کی صورت میں ددورا۔
Managements of Rice Blast:
It is essential to avoid the cultivation of diseased crops. Late planting should be strictly avoided to minimize the risk of disease development. After harvesting, it is crucial to eliminate any remaining straw and debris from infected crops, as these materials harbor disease spores. Additionally, the application of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers should be done in appropriate amounts to support healthy crop growth. It is important to maintain soil moisture and not allow the field to dry out for at least two weeks following the gourd stage. In the event that disease symptoms manifest, a treatment regimen involving azoxyservine and diphenoconazole at a concentration of 200 ml should be implemented, along with a spray of Fenoconazole at a rate of 250 grams per acre.
بیمار فصلوں کی کاشت سے بچنا ضروری ہے۔ بیماری کی نشوونما کے خطرے کو کم کرنے کے لیے دیر سے پودے لگانے سے سختی سے گریز کیا جانا چاہیے۔ کٹائی کے بعد، متاثرہ فصلوں کے باقی ماندہ بھوسے اور ملبے کو ختم کرنا بہت ضروری ہے، کیونکہ یہ مواد بیماریوں کے بیجوں کو روکتا ہے۔ مزید برآں، فصل کی صحت مند نشوونما کے لیے نائٹروجن اور فاسفورس کھادوں کا استعمال مناسب مقدار میں کیا جانا چاہیے۔ یہ ضروری ہے کہ مٹی کی نمی کو برقرار رکھا جائے اور لوکی کے مرحلے کے بعد کم از کم دو ہفتوں تک کھیت کو خشک نہ ہونے دیں۔ بیماری کی علامات ظاہر ہونے کی صورت میں، 200 ملی لیٹر کے ارتکاز میں azoxyservine اور diphenoconazole پر مشتمل ایک علاج کا طریقہ نافذ کیا جانا چاہیے، اس کے ساتھ 250 گرام فی ایکڑ کی شرح سے فینوکونازول کا سپرے کیا جائے۔
5-Rice Bakanae
The rice bakanae disease is attributed to the fungus Fusarium moniliforme. Plants affected by this disease exhibit stunted growth, a thin appearance, and a yellowish hue when compared to their healthy counterparts. Characteristic brown lesions develop on the stems, leading to rot that compromises the plant's integrity. The disease is primarily transmitted through the use of infected seeds and the presence of residual straw and plant debris from previous seasons. In severely affected plants, the leaves begin to desiccate from the base upwards, ultimately resulting in plant death. The stem undergoes decomposition starting from the nodes below the affected area, and a discharge may occur from the lump above the damaged section.
چاول بکائینی کی بیماری فُوساریم مونیلیفورم نامی فنگس سے منسوب ہے۔ اس بیماری سے متاثرہ پودے اپنے صحت مند ہم منصبوں کے مقابلے میں رکی ہوئی نشوونما، پتلی شکل اور زرد رنگت کی نمائش کرتے ہیں۔ خصوصیت والے بھورے گھاو تنے پر نشوونما پاتے ہیں، جو سڑنے کا باعث بنتے ہیں جو پودے کی سالمیت کو نقصان پہنچاتے ہیں۔ یہ بیماری بنیادی طور پر متاثرہ بیجوں کے استعمال اور پچھلے موسموں کے بقایا تنکے اور پودوں کے ملبے کی موجودگی سے پھیلتی ہے۔ شدید متاثرہ پودوں میں، پتے بنیاد سے اوپر کی طرف خشک ہونا شروع ہو جاتے ہیں، جس کے نتیجے میں پودے کی موت ہو جاتی ہے۔ تنا متاثرہ حصے کے نیچے نوڈس سے شروع ہوکر گلنے سڑنے سے گزرتا ہے، اور خراب حصے کے اوپر گانٹھ سے خارج ہونے والا مادہ ہوسکتا ہے۔
Managements:
The impact of this disease is significant, as it leads to wilting and eventual death of the plants. The fungus produces layers of white or pinkish-white mycelium, which contain millions of spores capable of infecting other plants. Occasionally, some tillers of the infected plants may survive, but they typically yield very few seeds. A small number of diseased plants can contaminate an entire field, resulting in widespread outbreaks in subsequent growing seasons. Therefore, effective management practices are vital to prevent the spread of rice bakanae and to ensure the health of future crops.
Management practices for Basmati and Shaheen Basmati varieties in infected fields should focus on utilizing resistant cultivars such as KS 282, KSK 133, and Nayab Ari 9. It is crucial to remove and properly dispose of any spring plants that show signs of disease. Seeds should never be collected from infected fields, and it is imperative to avoid transferring plants to nursery fields that are infested with pests. The application of a leaf-release fungicide is recommended as an effective strategy for managing blight, although spraying alone may not yield significant benefits.
اس بیماری کا اثر اہم ہے، کیونکہ یہ پودوں کے مرجھانے اور موت کا باعث بنتا ہے۔ فنگس سفید یا گلابی مائل سفید مائیسیلیم کی تہیں پیدا کرتی ہے، جس میں لاکھوں بیضوں پر مشتمل ہوتا ہے جو دوسرے پودوں کو متاثر کرنے کی صلاحیت رکھتے ہیں۔ کبھی کبھار، متاثرہ پودوں کے کچھ ٹیلرز زندہ رہ سکتے ہیں، لیکن وہ عام طور پر بہت کم بیج دیتے ہیں۔ بیمار پودوں کی ایک چھوٹی سی تعداد پورے کھیت کو آلودہ کر سکتی ہے، جس کے نتیجے میں بعد کے بڑھتے ہوئے موسموں میں بڑے پیمانے پر وبا پھیلتی ہے۔ لہٰذا، چاول کے بکانے کے پھیلاؤ کو روکنے اور مستقبل کی فصلوں کی صحت کو یقینی بنانے کے لیے موثر انتظامی طریقے ناگزیر ہیں۔متاثرہ کھیتوں میں باسمتی اور شاہین باسمتی کی اقسام کے انتظام کے طریقوں میں مزاحمتی کاشت کے استعمال پر توجہ مرکوز کرنی چاہیے جیسے KS 282، KSK 133، اور Nayab Ari 9۔ موسم بہار کے کسی بھی ایسے پودوں کو ہٹانا اور مناسب طریقے سے تلف کرنا بہت ضروری ہے جو بیماری کی علامات ظاہر کرتے ہوں۔ بیجوں کو کبھی بھی متاثرہ کھیتوں سے جمع نہیں کرنا چاہیے، اور یہ ضروری ہے کہ پودوں کو نرسری کے کھیتوں میں منتقل کرنے سے گریز کیا جائے جو کیڑوں سے متاثر ہوں۔ پتوں سے نکلنے والی فنگسائڈ کے استعمال کی سفارش کی جاتی ہے کہ جھلساؤ پر قابو پانے کے لیے ایک مؤثر حکمت عملی کے طور پر، اگرچہ اکیلے سپرے کرنے سے اہم فوائد حاصل نہیں ہوسکتے ہیں۔
6-Stem Rot of Rice
Stem rot, caused by the fungus Sclerotium oryzae, poses a threat to both rice and Basmati varieties. Symptoms typically manifest after the discharge of the fungus, with Sclerotia forming blackish-brown spots on the upper stem layer, particularly where it is submerged in water. As the upper layer decays, the disease progresses to the stem, leading to rot and eventual crop collapse. In cases of severe infection, the affected areas may not appear white, and cutting the stem will reveal numerous small black spots indicative of the fungal presence. The overall yield is adversely affected by this disease.
Managements of Stem Rot Disease:
To mitigate the impact of stem rot, it is essential to eliminate any midges present in the infected fields, as they can harbor the disease. Maintaining consistent water levels in the field for extended periods should be avoided, and water should not be transferred from infected fields to healthy ones. After 50 to 55 days post-transplanting, standing water should not be allowed to persist; instead, irrigation should be applied as needed. During land preparation, disease reservoirs may float on the water and accumulate at the field's edges, necessitating their collection and destruction to prevent further spread.
Sclerotium oryzae نامی فنگس کی وجہ سے ہونے والی ٹیم روٹ چاول اور باسمتی دونوں اقسام کے لیے خطرہ ہے۔ علامات عام طور پر فنگس کے خارج ہونے کے بعد ظاہر ہوتی ہیں، اسکلروٹیا کے ساتھ تنے کی اوپری تہہ پر سیاہ بھورے دھبے بنتے ہیں، خاص طور پر جہاں یہ پانی میں ڈوبا ہوا ہے۔ جیسے جیسے اوپری تہہ زوال پذیر ہوتی ہے، بیماری تنے کی طرف بڑھ جاتی ہے، جس کی وجہ سے فصل سڑ جاتی ہے اور فصل گر جاتی ہے۔ شدید انفیکشن کی صورتوں میں، متاثرہ جگہ سفید دکھائی نہیں دے سکتی ہے، اور تنے کو کاٹنے سے بہت سے چھوٹے سیاہ دھبے ظاہر ہوں گے جو فنگل کی موجودگی کی نشاندہی کرتے ہیں۔ اس بیماری سے مجموعی پیداوار بری طرح متاثر ہوتی ہے۔
اسٹیم روٹ بیماری کا انتظام:
تنے کے سڑنے کے اثرات کو کم کرنے کے لیے، متاثرہ کھیتوں میں موجود کسی بھی مڈج کو ختم کرنا ضروری ہے، کیونکہ وہ بیماری کو روک سکتے ہیں۔ کھیت میں پانی کی سطح کو طویل مدت تک برقرار رکھنے سے گریز کیا جانا چاہیے، اور پانی کو متاثرہ کھیتوں سے صحت مند کھیتوں میں منتقل نہیں کیا جانا چاہیے۔ پیوند کاری کے 50 سے 55 دنوں کے بعد، کھڑا پانی برقرار نہیں رہنے دینا چاہیے۔ اس کے بجائے ضرورت کے مطابق آبپاشی کی جائے۔ زمین کی تیاری کے دوران، بیماری کے ذخائر پانی پر تیر سکتے ہیں اور کھیت کے کناروں پر جمع ہو سکتے ہیں، مزید پھیلاؤ کو روکنے کے لیے ان کو جمع کرنے اور تباہ کرنے کی ضرورت ہے۔